**How Is Dew Point Calculated**
,文章长度约1000词左右。
html
How Is Dew Point Calculated
The dew point is a critical meteorological parameter that indicates the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to the formation of dew, frost, or fog. Understanding how dew point is calculated is essential for weather forecasting, agriculture, and even everyday comfort. This article explores the science behind dew point calculations and the methods used to determine it.
What Is Dew Point?
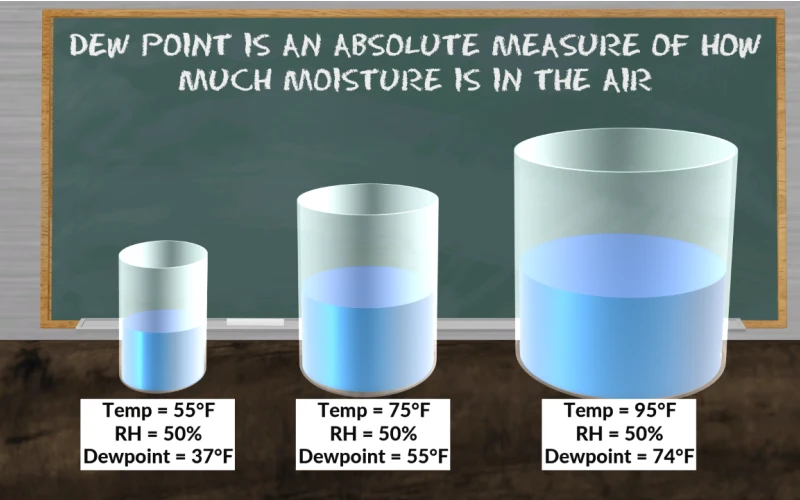
Dew point is the temperature at which air must be cooled for water vapor to condense into liquid water. When the air temperature drops to the dew point, the relative humidity reaches 100%, and moisture begins to form on surfaces. The higher the dew point, the more moisture the air contains, which can make conditions feel muggy or uncomfortable.
Factors Affecting Dew Point
Several factors influence the dew point, including:
- Temperature: Warmer air can hold more moisture, affecting the dew point.
- Humidity: Higher humidity levels mean more water vapor in the air, raising the dew point.
- Pressure: Atmospheric pressure can slightly alter the dew point, though its effect is minimal in most cases.
How Is Dew Point Calculated?
Dew point can be calculated using various formulas, depending on the available data. The most common methods involve temperature and relative humidity measurements.
Using the Magnus Formula
One of the most widely used formulas for calculating dew point is the Magnus formula, which approximates the relationship between temperature and dew point. The formula is:
Td = (b × α(T,RH)) / (a – α(T,RH))
Where:
- Td is the dew point temperature.
- T is the air temperature in Celsius.
- RH is the relative humidity (as a percentage).
- a and b are constants (typically 17.27 and 237.7°C, respectively).
- α(T,RH) is calculated as: (a × T) / (b + T) + ln(RH/100).
Simplified Approximation
For quick estimations, a simplified approximation can be used when relative humidity is known:
Td ≈ T – ((100 – RH) / 5)
This method is less precise but provides a rough idea of the dew point when detailed calculations aren’t feasible.
Using Psychrometric Data
In professional settings, dew point is often determined using a psychrometer, which measures wet-bulb and dry-bulb temperatures. These readings are then used in psychrometric charts or equations to derive the dew point.
Practical Applications of Dew Point
Knowing the dew point has several practical uses:
- Weather Forecasting: Helps predict fog, frost, and precipitation.
- Agriculture: Farmers use dew point to assess crop moisture and irrigation needs.</li
Keyword: how is dew point calculated